Special Episode: AI Hospitals - A Step Towards the Future
AI hospitals in Japan started as a project with a vision in which people can have access to high-quality healthcare anywhere in the country. It also aims to improve the well-being of healthcare providers, leading to compassionate patient care. Now, how far has AI hospitals come? Hospital care includes AI patient questionnaires, digital management of hospital beds, robotic drug dispensing and delivery, standing CT, robotic dogs powered by AI, and bed sensors that measure respiration and heart rate. Technologies are not limited to AI and involve robotics and digital technologies. Efforts using technology to eliminate disparities in healthcare are also gaining attention. For example, using AI to make a pathological diagnosis for cancer. Another is to use AI to identify the bacteria that cause blood poisoning. By feeding various images, AI is able to identify the types of bacteria in just 10 seconds at the level of a specialist. Reporter Michelle Yamamoto is joined by Dr. Yusuke Nakamura, an advocate of AI hospitals and a world-renowned expert in cancer immunotherapy and genetic research, to discuss the progress AI hospitals have made as well as the challenges they face.


Transcript
AI, artificial intelligence, finds cancer cells.
A robot delivering medicine.
An AI robot providing comfort to sick children.
Efforts are underway to use AI and other digital technologies to make patient experiences at hospitals more comfortable.
They ease the burden on healthcare providers, reduce medical errors, and lessen rural health disparities.
Several leading hospitals in Japan are participating in this project, turning various ideas into reality.
The project is led by this person.
We need AI and digital technology to improve
the wellbeing of doctors and patients alike.
The main goal of this project is to bring
empathy and compassion back to healthcare.
How will AI transform hospitals?
What will the future of hospitals look like?
On today's Science View, we will look at the forefront of AI hospitals in Japan.
Hi, I'm Michelle.
When you are feeling slightly ill, you might find it a burden to go see a doctor at the hospital.
In Japan, there is a long waiting time, a brief examination with the doctor, and the hassle of undergoing tests.
As a result, some may feel reluctant to go see a doctor.
Doctors, on the other hand, often say that they would like to spend more time to examine patients, but are too busy with other tasks.
Efforts are underway to solve these problems, making hospital visits less burdensome and more pleasant.
It is known as "AI Hospital."
Today, I am visiting an institute in Osaka to meet Yusuke Nakamura, an advocate of AI hospitals.
Let's go and meet him.
Hello.
Hi, nice to meet you.
Nice to meet you.
Welcome to Osaka.
- Thank you very much for having us today.
- Please follow me.
So, an AI hospital is a term that is still unfamiliar to many of us in Japan.
Can you explain what AI hospitals are exactly aiming to achieve?
You know, the "AI" means "ai" in the...
"love" in Japanese.
Yes.
So, now the humanity is little bit less in the medical area.
So, my aim is to bring back the humanity in medical care system by supporting AI or digitalization.
So, we prefer the term of "AI hospital" because of, as I mentioned, connected to love in Japanese.
That's a wonderful idea.
And are there other things that you try to keep in mind for the doctor's sake or the patient's sake?
Actually both.
When you go to the examination room in hospital, so in general doctors are just looking at the keyboard and monitor.
So, there almost no time to watch each other.
And basically now the eye contact is lost in the medical examination room.
But that increase the unsatisfaction of the patient.
So, if we can have extra time or enough time to take care of patient,
we can watch at the patient and basically understand how they feel emotionally and can take care of the patient with humanity.
That is the biggest goal.
What would an AI hospital be like overall?
I had a chance to experience it.
Let's go look.
At Keio University, one of Japan's leading universities in medicine, the entire hospital is pushing toward digitalization.
First you sit down and it's just like a smartphone.
It tells you what to do.
Okay, so I have three choices.
Uh, this is where you draw blood.
Let's go.
With this, patients can easily move around the spacious hospital.
Oh, another one.
So it's another a minute and 30 seconds for me to ride this.
We're here.
The wheelchair automatically goes back to its station.
New patient questionnaire is conducted on a tablet.
Data is then transferred to the patient's medical records.
In the future, the goal is for AI to automatically assess what disease the patient may have.
Instead of checking textbooks, we can find
digitized information in the medical records.
An ultrasound of the final stages of pregnancy.
The baby is practicing breathing
which is a good sign.
It's doing a little fist pump.
As soon as the doctor sends the data, the images can be seen on an app.
Various data on the patient is saved on it.
In the beginning, there was concern that
it would complicate things and slow us down.
But when we tried it, it was very smooth.
Hello.
With this app, the mothers can also get postpartum consultations remotely.
It all started when the Covid-19 pandemic restricted outpatient admissions.
Providing support to mothers became difficult.
Something had to be done quickly.
Hospital patient management has also been digitized.
Hospital bed occupancy rate in each ward is updated every 15 minutes.
The system also predicts how many beds will be occupied in the next four weeks.
This will help us achieve our goal of
reaching over 90% bed occupancy rate.
A robot scans prescriptions and prepares medication for each in-patient.
Is the robot picking up medicine
from various shelves?
Yes. Based on the prescription data,
the arm pulls out the medicine
and cuts the sheet.
After the medicine is placed in the box,
a pharmacist double checks to ensure safety.
This robot delivers the medications from the pharmacy to the hospital wards.
It summons the elevators wirelessly, allowing it to move to different floors.
In this project, efforts are also being made to develop equipment that help reduce the burden on patients.
This CT scan does its job while the patient is standing in an upright position.
Patients can be scanned after entering the room, without having a technician be present.
Let me just slide in here.
Yes. Stand with your back against the pole.
Okay.
That should keep you steady.
It cut the necessary hospital examination time in half.
Wait! That's it?
It's so quick and easy.
For patients, it's very easy and
they have less exposure to radiation.
For doctors, it eliminates unnecessary contact
and they can operate the machine remotely.
For hospitals, it takes up less space.
At first glance, this is just a bed.
But in fact, it can take measurements such as respiration and pulse just by lying on it without attaching any special device on the patient.
The sensor in the thin metal panel
detects the change in weight
as the heart beats or the patient breathes.
That's how heart rate
and respiration are measured.
Measurement results can be viewed remotely through a monitor.
It's quite stressful for patients
to wear a heart monitor all the time.
Being able to monitor the patient's condition
in a contact-free manner will greatly improve
the quality of medical and nursing care.
A patient is being examined a day after a heart surgery.
She will have to continue her electrocardiogram, or ECG, for some time.
Up until now, patients have worn this device 24 hours a day.
It's quite heavy and gets caught
in places like this.
People may live far away or be busy with work.
Many feel reluctant to do an ECG
for various reasons.
As a solution, this new T-shirt-type ECG can be sent to the patient's home instead of them coming to the hospital.
It allows easy measurements and easy mobility.
This won't get caught in things.
I've told my doctor I'd like to try it.
This hospital specializes in treating children.
In Japan, a vehicle with a doctor on board to transport urgent patients is called a "doctor car" or a "mobile ICU."
Blood pressure 97 over 27.
Heartrate 152.
The doctor starts treatment in the vehicle.
The AI recognizes the doctor's voice and automatically records what the doctor says about the vital signs
and the treatment being performed into the medical record.
Until now, record keeping required manual data entry.
This lets me keep
important and acurate records
even when my hands are full.
Many children stay at this hospital for their treatment.
This robotic dog powered by AI is their playmate.
Amazing!
The robot learns words and actions and responds according to each child.
That's cool!
If the robotic dog can spend 15-20 minutes
with a child about twice a week,
it learns about the child and can play
in a way that is suited to that child.
Children feel secure, because they can
share their feelings of pain and sadness
with this dog-shaped robot;
things that are hard to tell your doctor
or your parents.
Come here.
After a major surgery, Chisako was hospitalized for a long time and felt scared because she couldn't see her family much due to the pandemic.
I was lonely and scared, but this robot
told me everything was going to be okay.
It seems to sense what I was feeling.
I was able to endure the surgery
and my long stay because of this dog.
So, many different technologies are being used.
I didn't realize how broad and far-reaching AI hospitals can be.
However, it has not yet reached 100 percent reliability in the field of medicine.
A small mistake can be fatal, right?
At the beginning, the AI can provide maybe 70 to 80% accuracy.
If we can educate AIs using high quality data, so accuracy will be higher and higher.
One example, mammography.
It's breast cancer screening.
Two doctors need to read mammography data.
But in local hospital, there are not many specialists.
But if we can ask AI to read, and the specialist can read, and they combine,
they can provide more accurate data.
But in the time being, I'm sure that not very many hospitals can do that and the country can't support that many hospitals.
The one of the goals is to make a system that every doctor can access to the high quality AI systems.
Hospitals are working to provide high quality diagnosis and advanced treatments.
This is a hospital specializing in cancer treatment.
Requests for pathological diagnosis of cancer arrive from all over Japan.
They confirm if the patient has cancer or not and examines the type of cancer and its spread.
Making a diagnosis by looking at cells under a microscope requires technique and experience, and human resources are limited.
It is also time consuming.
Now, research has begun that uses AI for making pathological diagnosis.
So far, it has been trained on data from 200,000 data images of cancer cells.
Here is a specimen that's hard to tell
how far cancer has spread.
This AI reading shows that
the blue area is likely to be cancerous.
On the right is the digital data
of the pathology slide from this specimen.
AI determined that there are cancer cells
in this blue area.
If we zoom into this area,
we can Find cancer cells.
What looks like grayish-white frog eggs
are undifferentiated cancer cells.
This type spreads through the mucous membrane
of the stomach in a scattered way
making it difficult and time-consuming
for doctors to find.
AI accurately determines that this area is cancerous.
However, this AI is still in the development stage,
so it's not perfect.
As you can see, there are
undifferentiated cancer cells in this area,
but AI is not yet able to detect that part.
By teaching AI that this area is also cancerous,
it will learn and be able to recognize
next time there are cells like this.
So in the next step, we can expect
AI to be smarter than it is now.
Our mission is to develop AI so that
other hospitals can have the same level of
treatment and diagnosis as our institute.
We want to spread this knowledge
to other hospitals and society.
Meanwhile, the National Center for Child Health and Development is working on having AI identify bacteria types in less time.
Minori developed blood poisoning, or sepsis, after a bone marrow transplant.
Doctors quickly identified the bacteria that caused the infection and she was able to recover.
She was doing great, then suddenly,
she was in the ICU.
I was suffering and they hooked
up lots of IVs. So I started to panic.
In the world, roughly 50 million people suffer
from sepsis annually,
and about 10 million die.
It's crucial to identify the cause of the infection
as soon as possible and start treatment.
It takes about 3 days to culture enough bacteria.
Waiting that long could be too late.
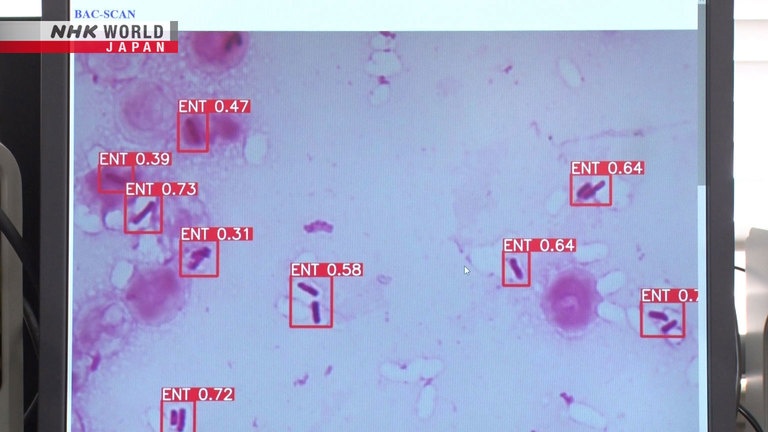
At this hospital, they developed a system that allows AI to identify the bacteria from pictures taken after about one day of culture.
It takes about 10 seconds to get the results.
This red bar is the bacteria.
AI first determines where the bacteria are.
ENT indicates that the bacteria are the types
found in our gut, such as E.coli.
The numbers show how likely the bacteria
appear to be present.
Even doctors in small remote hospitals can take microscopic pictures with a smartphone and access this hospital's AI for identification.
Even without fancy cameras,
we can do as well as a skilled technician
or an infectious disease specialist
in just about 10 seconds.
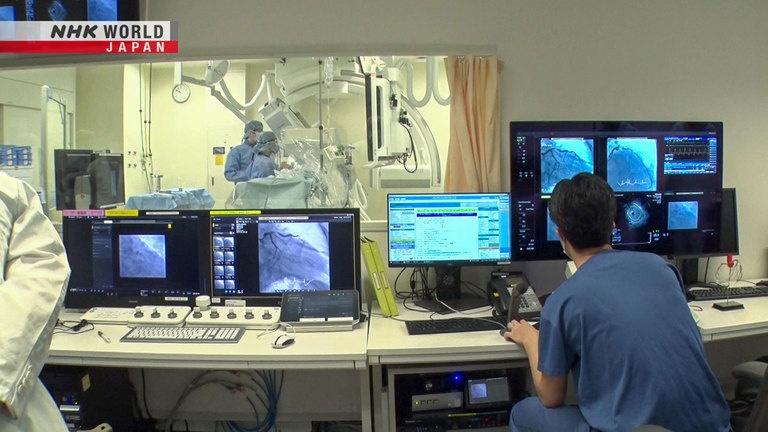
At Keio University Hospital, a robot is used to expand blood vessels in patients with heart disease.
This is the robot.
The robot inserts a catheter into the blood vessel and widens it with a short tube called a stent.
Until now, this procedure had been performed by doctors,
and it was necessary to avoid exposure to radiation as it was performed while using X-rays.
We wear this lead-containing protector
to reduce exposure to radiation.
But they are heavy and puts strain
on the shoulders and the lower back.
This protects the thyroid glands
and the glasses reduce the risk of cataracts.
In contrast, we operate the robot from the outside
so the protectors can be removed completely.
It's also beneficial to the patient as we can
control stents and balloons with precision.
This could reduce radiation exposure
and also the amount of contrast medium used.
While assistants are still needed to provide help near the patient, the main doctor operates from back here.
This is the control console.
The middle controller moves the wire
and the left one controls the balloon and stent.
This patient has a narrowed blood vessel.
They will perform a procedure to expand it.
First, a wire serving as a guide is inserted deep into the blood vessel.
Next, a catheter is inserted and a balloon is used to inflate the narrowed area.
A stent is inserted.
This is a stent.
This is how the blood vessel is kept open.
Like this. The stent helped open the artery.
As you can see, the narrow area has expanded.
With this method, the procedure could be performed remotely by a skilled physician in the future.
We are hoping to be able to treat patients
in rural areas with remote operation.
I have six months experience in Shodoshima Island.
So, actually, I experienced what is the medical condition in island.
So, because of that kind of experience,
I wish to provide same quality of medical care system in all over the Japan.
And if we can make these kind of system, so we can export this kind of very elegant healthcare system to many countries.
I think in the 10 or 20 years, I think kind of the internet hospitals will be established so patient need to go to hospital when they need.
So, I think medical systems or medical care providing systems, now they're very rapidly and drastically changing.
Yume was born without fingers on her left hand.
She has begun using an AI-powered robotic hand.
AI moves her prosthesis by learning the electric current that flows through Yume's muscles.
Oh! You did it.
Well done.
The AI robotic hand was developed by Dr. Yamanoi and his group.
Until now, moving a robotic hand
required the patient to work hard
to generate muscle activity every time.
With AI, it learns each patient's muscle activities
and remembers the matching movement.
So the patient can move the robotic hand
fairly quickly after putting it on.
With this sensor, the AI catches the amount of electrical signal and frequency generated by the muscles.
And the AI learns to help move the robotic hand as intended by the user.
Similar to eyeglasses,
if you have poor eyesight,
wearing glasses will help you
lead a normal daily life.
I hope to use such technology
to make life easier for people with disabilities.
Yume started 2nd grade this spring.
She can even do pullovers on bars.
However, there are some things she cannot do without her robotic hand.
She continues her training.
Now, Yume can hang out the laundry and dress up dolls.
When I can't do things
that others can do, I feel upset.
When I can successfully do things using this,
I feel like I caught up with them.
Her competitive nature is an advantage.
AI robotic hand is giving us hope
and opening up various possibilities.
AI hospital is gradually transforming healthcare and hospitals across Japan.