1) How the Diet works
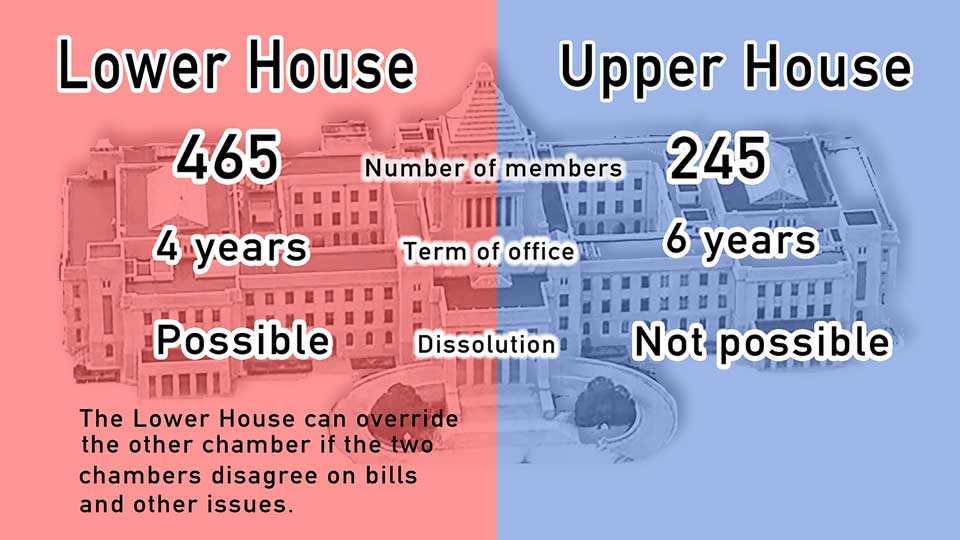
Japan's Diet is made up of two chambers: the Lower House, or House of Representatives, and the Upper House, or House of Councillors. In principle, legislation must be approved by both houses, but the Lower House has the ability to override the Upper House.
2) Dissolution of the Lower House
There are two ways to dissolve the Lower House.
The chamber can pass a non-confidence resolution, or the Prime Minister can decide to dissolve it and trigger a general election. That power is often referred to as "the last trump card" of the Prime Minister.
When the Lower House is dissolved, all 465 members lose their seats, and those seats are contested in a general election.

3) How winners are elected
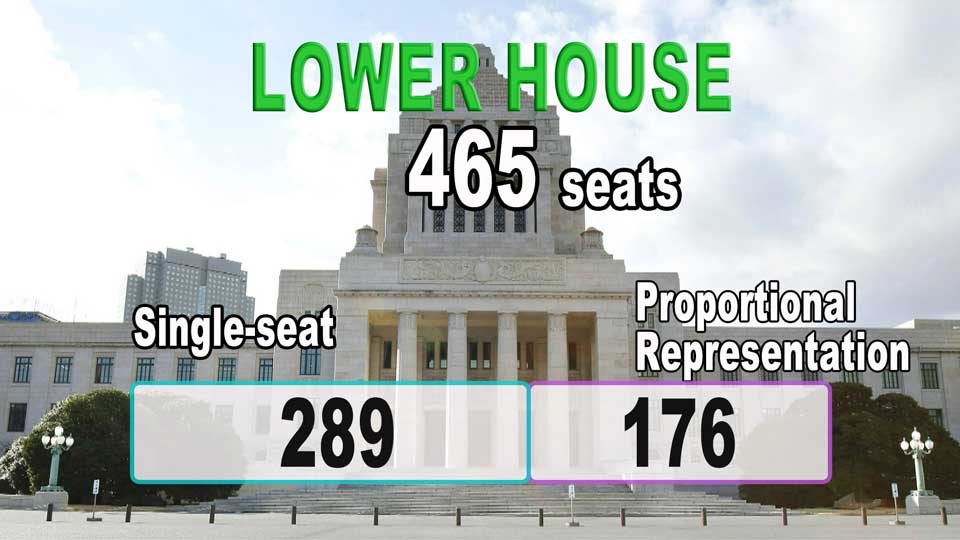
Of the 465 lawmakers, 289 are elected from single-seat constituencies using a first-past-the-post system. The remaining 176 seats are allocated through a proportional representation system in 11 blocks nationwide.
Lower House lawmakers have four-year terms, but those terms can end at any time if a prime minister wishes to call a general election.
4) The timing of the vote
Prime Minister Kishida Fumio dissolved the Lower House on October 14, just 10 days after taking office.
That is the shortest period on record under the current Constitution. The official campaign period started on October 19. Voting will take place on October 31.


